Traditional television has been in decline for several years now due to the changing global trends and technological development. The widespread availability of the internet has made everything more accessible, including TV. Nowadays, you can access your favorite shows and movies at will, thanks to internet protocol television (IPTV). Since convenience is the number-one consumer need in today’s fast-paced world, IPTV has quickly conquered the market due to its superior user experience.
But what is IPTV exactly? How does it work? Is it all positives and no negatives? These are just some of the questions we’ll address in this article.
Let’s start with the basics.
What Is IPTV?
IPTV stands for internet protocol television and uses the technology that delivers live television programs over the internet instead of antennas, satellite dishes, or fiber-optic cables. In other words, IPTV streams video content in real time over the internet.
Although IPTV content delivery differs from online video-sharing platforms like YouTube or OTT services like Netflix, it shares many of their conveniences. For instance, IPTV allows users to access video on demand (VOD) content on a subscription-based model and watch live broadcasts. That gives viewers the freedom of accessing their favorite shows at will while still having the option of enjoying live events and programs like on traditional TV.
This flexibility is why IPTV outshines traditional television and is considered the future of TV.
How IPTV Works
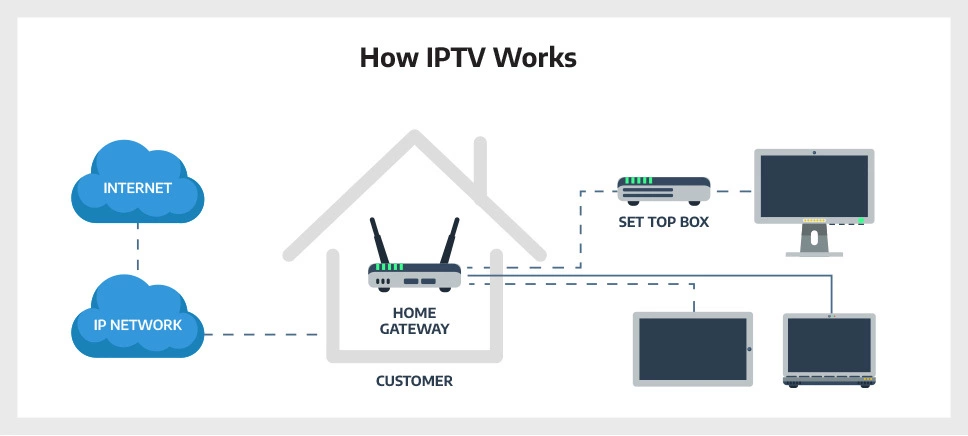
While traditional TV sends analog signals to users via cables, IPTV sends them over a managed, private internet network. Unlike traditional TV, which can only broadcast content in real time, IPTV has servers for storing content. That gives users the freedom to watch programs at will (if their IPTV provider allows this option).
The entire content delivery process is quite simple and can be illustrated in a few steps:
- The user requests to watch a specific program, and the IPTV provider receives the request.
- IPTV provider processes the request and transmits a video stream from their server to the end user.
- The content stream travels through the secure, private network toward a gateway on the user’s end.
- The content is delivered in packets to the playback device via the real-time streaming protocol (RTSP) before compressing them to optimize for playback.
But for all the above to be possible, your TV must be able to read the signals received over the internet protocol. Unfortunately, not all TVs can set up an IPTV service right off the bat since most can’t read the signals received without external help. If you have a TV set that isn’t IPTV compatible, you will have to buy an IPTV set-top box.
What Is an IPTV Box?
An IPTV box or a set-top box is a device that converts streaming signals received via the internet protocol into a format that a TV can read and reproduce (similarly to an OTT box). In other words, set-top boxes translate the language of the internet protocol. These boxes are often connected to the TV via HDMI or AV cables or even through Wi-Fi for newer models.
If you choose to stream IPTV from your computer, you won’t need a set-top box as PCs can already read the data received through the internet protocol. Those who’d like to save on a set-top box but still enjoy watching IPTV on their television screens can mirror their PC screens on the TV and watch from there.
Hybrid IPTV
The high demand for internet-based streaming services and on-demand shows led to the rise of a new, hybrid IPTV business model. Hybrid IPTV proved the perfect way for traditional broadcasters to transition to a more contemporary business model.
Since traditional TV broadcasters needed to adapt to changing consumer behavior, this model enabled them to continue providing traditional TV services while combining it with the on-demand model most OTT platforms use.
The hybrid IPTV model allows users to watch linear TV and on-demand content with a single set-top box. This model’s most significant benefits are its flexibility and affordability since neither users nor providers need to constantly change their infrastructure.
Users can freely opt in or out of different features without needing to change their set-top box, and providers can introduce updates and new services at a minimal cost. Either way, it’s a win-win scenario.

Types of IPTV Formats

IPTV offers many additional services and video formats beyond just watching traditional television broadcasts. There are three primary content formats most IPTV services offer:
Live TV
Live IPTV allows users to live stream television broadcasts in real time, similar to traditional TV. Live TV most often serves to broadcast live events like sports events, conferences, etc.
However, this model has the same downsides as the dying cable TV. Users can’t choose when to watch content, and they don’t have the flexibility of watching it on the go.
Some examples of IPTV providers with this model include FOX Sports Go, Hulu Live TV, Sling TV, and CBS Sports HQ.
Video on Demand (VOD)
VOD IPTV services work the same way as with most OTT providers — you pay a subscription fee and, in return, have access to a large library of videos you can request to watch whenever.
This model is particularly appealing to consumers because it offers incredible flexibility. More and more IPTV providers have been introducing on-demand services to combat the growing popularity of over-the-top streaming platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video.
Time-Shifted TV
Time-shifted TV or catch-up TV is a service unique to IPTV that allows users to watch previously broadcasted TV shows later.
There’s one big difference between time-shifted TV and VOD, though. Time-shifted TV lets users rewatch old content only for a limited time. Most often, broadcasts will be available for a few days before disappearing. Anything older than that would be considered a VOD.
One of the most popular IPTV providers using this model is BBC’s iPlayer.
Advantages and Disadvantages of IPTV
Although IPTV offers incredible flexibility and user experience, there’s much more to it. It’s also vital to look at both sides of the coin here, as IPTV isn’t perfect either. Here are some of the most notable pros and cons of IPTV:
Pros:
- Easy to Set Up and Use — All you need to get started is to buy a set-top box and connect it to your TV set. Also, the Wi-Fi connectivity that newer models have makes the process significantly easier.
- It Is 100% Digital — The world is becoming more digital-oriented by the day, so transitioning to digital TV is an excellent foundation for the future and new tech.
- IPTV Allows Smooth Simultaneous Streaming of Multiple Programs — IPTV services let users stream multiple programs simultaneously on different devices (TV, PC, etc.).
- Variety of Service Types — The multiple types of services IPTV offers exist to fit different consumer tastes.
- Allows Users a Commercial-Free Experience — Many people hate advertisements, so being able to skip or fast-forward them is an excellent quality-of-life improvement.
- Incredibly Time-Efficient — Not having to wait for specific times to access your favorite broadcasts and skippable commercials is why IPTV is so appealing to users worldwide.
Cons:
- Network Overloads May Cause Technical Issues — If too many users watch a specific show simultaneously, the network may overload and cause buffering or playback issues.
- Users Have Little to No Control Over Channel-Related Issues — If an error occurs on a channel’s end, there’s little to nothing viewers can do to fix the issue but wait.
- Synchronization Problems Are Commonplace – Due to natural fluctuations in network speed and quality, viewers may experience synchronization problems. If these occur, they deal a massive blow to the quality of user experience.
As you can see, IPTV isn’t omnipotent and has a few downsides to traditional TV. But since technology keeps developing rapidly, we wouldn’t be surprised if these few issues got dealt with sooner than later. Besides, the UX improvements IPTV brings to the table far outweigh these potential problems, wouldn’t you agree?
IPTV Service Providers
There are hundreds of IPTV service providers out there, and the features and programs they offer will vary greatly depending on your country or state. Here are some of the most popular IPTV providers in the U.S.
- Xtreme HD IPTV
- Bestbuy IPTV
- Comstar
- Apollo Group TV
- Necro IPTV
- Tubi
- Vudu
- The Players Klub
- Falcon TV
- IPTVtune
Note: Before you start looking for an IPTV provider, you should first check if IPTV is legal in your country or state. Although IPTV is legal in most countries, there are some bad actors on the market that you should avoid at all costs.

The Valuable and Rapidly Growing IPTV Market Size
The IPTV market size is massive, and new providers are entering the industry daily. That is part of the reason the demand for IPTV is growing rapidly. Here are a few IPTV statistics to better illustrate the market’s rapid growth:
- The demand for IPTV services is increasing at an annual rate of 30%–35% globally.
- There are currently more than a billion subscribers to IPTV services worldwide.
- IPTV is most popular in European countries like France, Germany, and the U.K. These countries currently have the largest IPTV market share.
- India is the fastest growing IPTV market currently and will likely pass its European counterparts in a few years.
The biggest reason for the boom of the IPTV market is the massive advertising potential it has. Advertisers can use IPTV to get in front of millions of viewers worldwide they can’t reach by other means. That is why most IPTV services operate on an advertising video-on-demand monetization model.
Is IPTV the Future of TV?
Despite IPTV’s constant growth, its future is challenging to gauge. The reason is that IPTV directly competes with the even more popular OTT and CTV industries.
These industries are growing even faster than IPTV and are a force to be reckoned with. Although the future of TV undoubtedly lies in online video delivery, we have yet to see which technology will take the throne. As things stand right now, we can only make an educated guess.
How IPTV Compares to OTT and CTV
Although both IPTV and OTT deliver content over the internet, they use different technologies. With each of those technologies come different benefits and downsides.
IPTV operates in an isolated, private ecosystem, making it superior to OTT’s delivery method, which relies on open internet networks. Since OTT relies on your internet’s bandwidth, it is more prone to lag or connection breaks than IPTV. Similarly, this technology also enables IPTV to deliver higher quality content than you could get with OTT.
However, OTT has several huge advantages over IPTV, like better accessibility, a higher variety of video monetization models, and lower infrastructure and maintenance costs for providers.
Around 65% of users stream videos on mobile and TV apps nowadays in favor of TV or browsers. That means it’s more important than ever to be accessible to users across these devices, which OTT easily allows (through OTT apps).
At the same time, OTT monetization is more flexible. Providers can opt to monetize with ads, subscriptions, or even pay-per-view models.
Another massive upside to OTT is that it doesn’t require expensive infrastructure and maintenance. These lower initial costs are what make OTT more appealing to newcomers in the video streaming world.
With the above in mind, we can’t help but wonder if IPTV can stay competitive with OTT for much longer unless something drastically changes.
Is Getting Content on IPTV a Good Choice for Your Broadcasting Business?
With everything we discussed so far, we’d have to say this decision is entirely up to you. The easiest way to decide would be to figure out if you value reach or content quality more.
If you’d rather deliver the best service possible despite higher costs and lower reach, then, by all means, start an IPTV service.
On the other hand, if you prefer going global and offering an easily accessible service that will appeal to broader audiences, then OTT is likely the better choice.
And if you decide to go the OTT route and build an OTT app or streaming service, Brid.TV can help you. Publishers and broadcasters can use our white-label OTT apps to easily launch an ad-supported app across Android, iOS, Android TV, Apple TV, or Samsung and LG smart TVs.
The Brid.TV online video platform was built from the ground up to help publishers and video providers maximize website, OTT, and CTV ad revenue. So if your goal is to launch an ad-supported OTT service, get in touch, and we’ll help you make that goal a reality.

FAQ
1. What does IPTV stand for?
IPTV stands for internet protocol television. The IPTV technology delivers content through a closed, private network instead of antennas, satellite dishes, or fiber-optic cables.
2. What’s the difference between IPTV and linear TV?
The difference between linear TV and IPTV is that users can only consume linear TV synchronously (at a set time on a set TV channel), while IPTV can also include on-demand content and time-shifted TV.
3. Is IPTV the Future of TV?
IPTV’s future is challenging to gauge due to the unprecedented growth of its primary competition — OTT and CTV.
4. Are IPTV services available in all countries?
IPTV services are available in most countries and states. However, you should always first research providers in your area before picking one.
5. Should you use a VPN with IPTV services?
Using a VPN can help you access IPTV services that may be blocked by your Internet Service Provider. However, make sure your desired IPTV service supports VPNs before using one.

